 Uncategorized
Uncategorized
 Uncategorized
Uncategorized

 Publications
Publications
Liu, X. et al., Circulation in press
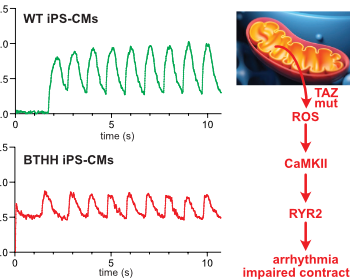
Barth syndrome cardiomyocytes from human iPSCs and mice have abnormal calcium handling that is partially due to activation of CaMKII. Barth syndrome mice had increased vulnerability to arrhythmia, perhaps reflecting the abnormal calcium handling.
 Publications
Publications
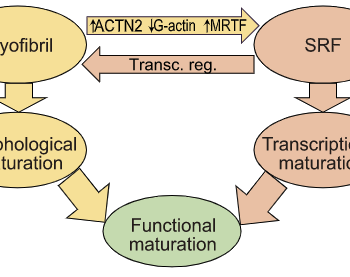
Sarcomere assembly promotes MRTF-SRF signaling to drive a feed-forward circuit that stimulates cardiomyocyte maturation.
 Uncategorized
Uncategorized
 Publications
Publications
Wang, S et al., Circ. Res. in press.
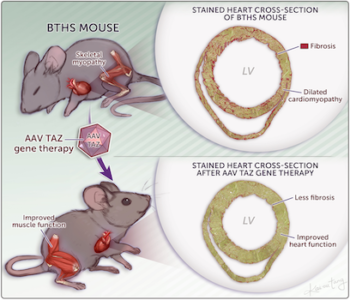
AAV gene therapy improved survival and heart and skeletal muscle function in a new mouse model of Barth syndrome.
 Uncategorized
Uncategorized
in press in Circulation Research.
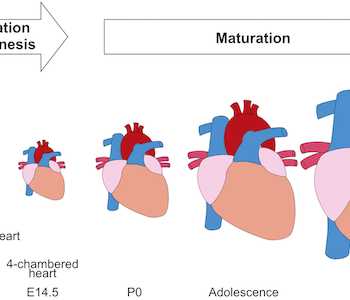
Cardiomyocyte maturation is the process whereby proliferative and glycolytic fetal cardiomyocytes become specialized to forcefully and efficiently contract billions of times in an animal’s lifespan. This review article by Yuxuan Guo and William Pu summarizes our current understanding of mechanisms that promote and coordinate the process of cardiomyocyte maturation.